Managing Unbound DNS overrides with Boundation
Boundation GitHub repository
At some point in the past six months or so I’ve started using a mini pc with OPNsense installed as my router. I’ve replaced AdGuard Home with Unbound DNS running on the router. It provides all the blocklist functionality I want, plus Unbound integrates quite well with the DHCP server.
Generally I like Unbound, but managing DNS changes automatically has proven more challenging than with AdGuard Home. With AdGuard home I used ExternalDNS and the External DNS - Adguard Home Provider (Webhook) to automatically manage DNS entries for my Kubernetes deployment. No such option seems to exist for Unbound.
So I built Boundation. That’s the best name I could come up with. Let’s not talk about that.
Requirements
- DNS entries must be created for environments as they’re spun up. For example, if I open a PR for one of my web projects, a test environment is created with a new ingress. My internal DNS must be updated with the appropriate records.
- DNS entries must be removed when environments are destroyed. When I merge the example PR, the test environment is automatically torn down. The DNS record must also be cleaned up.
- Bonus: Ability to manage DNS for services outside of Kubernetes.
Initial Solution
I created an External DNS Webhook for Unbound using the OPNsense API. When I deployed it with External DNS, I found that duplicate DNS entries were constantly being created. I had either misconfigured External DNS, or done something wrong. Either way, I realized External DNS was overkill. The only time I need a DNS entry to change is when I Create, Update, or Delete a deployment.
Simplified Solution
I took the work I’d done for the webhook and created a simple CLI. Some simple usage examples:
Create or Update overrides:
| |
Read existing overrides
| |
Delete overrides
| |
Run interactive configuration menu
| |
Source code for both solutions can be found in the boundation repo.
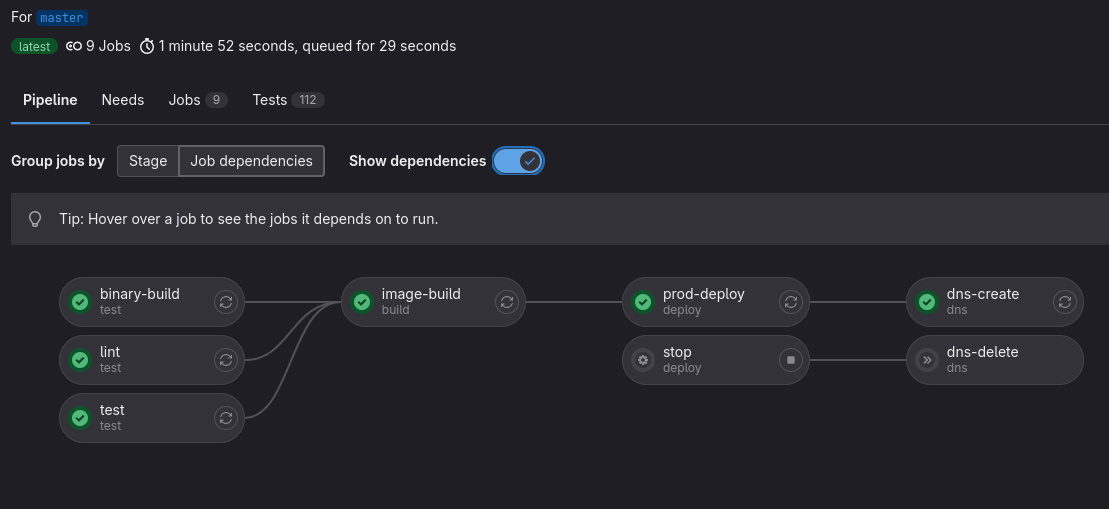
Example snippets for GitLab CI
I use GitLab for my internal projects, so here’s an example .gitlab-ci.yml snippet for pull request deployments, creating the DNS entry then deleting the entry when the environment is stopped.
| |
Example cli config. You can get the API key in the OPNsense UI under System -> Access -> Users -> ${USER} -> click the + button in the API Keys section.
| |
Obviously the script sections above can be pulled into more reusable scripts, this is just an example afterall. The snippet above is 90% of a fully automated environment deployment and DNS management with GitLab CI.